Since a few month, I own an Elegoo Mars Resin printer. It has UV LCD screen for “printing” each layer. In addition, I have an Elegoo Mercury Wash & Cure machine for a few weeks. These machines are incredibly affordable, they work and have a high resolution. The print space is rather small (120 (L) x 68 x 155 (H)…
Category: Tinkercad
BI2 – building a silicone sex toy
Now let’s build the first ESP8266 vibrator. I use the reliable design from this blog post and the new BI2 board. The new BI2 board can be controlled from any smart phone or computer.
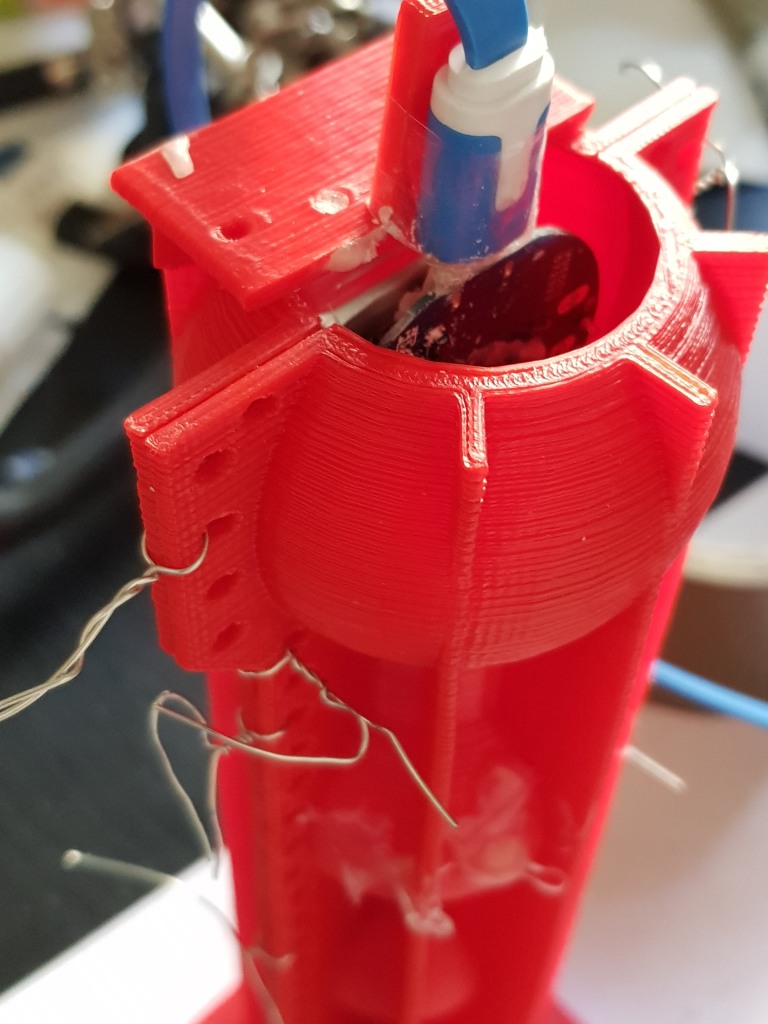
As the BI2 board is round there is no need to build a case for the PCB and the LiPo. The easist way is to glue the battery directly on the ESP8266. Connect the battery and one or more vibration motors with the BI2 board.
The form consists of two parts which are fastened together with tinker wire. Before you have to insert the board with the vibration motor(s) and the battery. Therefore I used a handle. The handle could be put on top of the form. Then fix a USB connector to the handle. Plug in the BI2 board. Fasten the second half of the form.
Very important: The USB micro connector on the board must be protected from the silicone. When silicone flow between USB plug and connector it will be impossible to pull out the plug. I use wax to seal the USB micro connector. Read more here.
Now pour in the silicone, wait for some hours. And open softely the form.
Remove the overhanging silicone.
Here ist the Link to Tinkercad where you can edit the form and download STL files for your 3D printer: Download from Tinkercad: form, handle. Download ready to print zipped STL files.
Now build YOUR personal sex toy. Here you find the code for the ESP8266 as well as an IOT server application for quantifying your sex and remote control.

Basic Node for the Internet of Sex Toys – part 2: 3d printed form, assembly, molding
 In this series of posts we describe how-to make a vibrating sex toy which is part of the Internet of Things.
In this series of posts we describe how-to make a vibrating sex toy which is part of the Internet of Things.
part 1: Basic Node for the Internet of Sex Toys
part 2: Molding the Basic Node
part 3: Software for the Basic Node
In part 2 we describe how-to make a mold form for the basic node. We need three forms:
- the mold form which consists of two parts
- the inlay which protects the electronics of the basic node
- a “hanging” for the inlay
We used Tinkercad to construct the parts. The molding form is based on Tinkercad’s banana form. You can edit and share them from your browser:
Inlay: https://tinkercad.com/things/h5fFOBqlmjw
Hanging: https://tinkercad.com/things/jUxc2oAamww
Form: https://tinkercad.com/things/6HS3XScOsCM
Instructions
Print out all forms. The STL files are available at Thingiverse. You might want to use XTC or similar for smoothing the inner part of the mold form.
Assembling the Inlay
We use the inlay to protect the electronics.
 Simply put the electronics inside so that the upper body of the switch is on the same level as the upper inlay. We use hot glue to fix the basic node.
Simply put the electronics inside so that the upper body of the switch is on the same level as the upper inlay. We use hot glue to fix the basic node.
 Then fix the receiver coil of the wireless charging module on top of the inlay. The next step is to fix the hanging at the inlay.
Then fix the receiver coil of the wireless charging module on top of the inlay. The next step is to fix the hanging at the inlay.
 Now fix the LiPo battery on the bottom side of the inlay using hot glue or similar. Fix the wires. Finally you might fix the wires of the vibration motor next to the middle of the LiPo battery.
Now fix the LiPo battery on the bottom side of the inlay using hot glue or similar. Fix the wires. Finally you might fix the wires of the vibration motor next to the middle of the LiPo battery.
 Use tinkering wire to fix both parts of the molding form.
Use tinkering wire to fix both parts of the molding form.
 Put the inlay in the form. Fix the hanging with a tape or similar. The motors shouldn’t touch the inner part of the form.
Put the inlay in the form. Fix the hanging with a tape or similar. The motors shouldn’t touch the inner part of the form.
 Now prepare the silicone. We use Shore A 45 silicone (approx. 250 ml) from Silikonfabrik.de. It is hard but still a bit flexible. You may add color, too. You have about 10 minutes to stir the silicone and poor it in the form.
Now prepare the silicone. We use Shore A 45 silicone (approx. 250 ml) from Silikonfabrik.de. It is hard but still a bit flexible. You may add color, too. You have about 10 minutes to stir the silicone and poor it in the form.
After some hours you can remove the form. As you can see there is overhang which make removing the form very hard. The form could break when removing. Better preparation of the form (eg rasping) could improve the results.
If the blue LED of the Wemos board is still active you were successful.
Now you need a charging station. The construction is shown here. It is also possible to connect the sender (or transmitter) module with a 5V power source (eg. from the USB port). Just put the bottom of the molded basic node on the sender coil.
In the next part we introduce an updated version of the software including over the air update and WiFi management.
OpenSCAD as silicone molding form generator

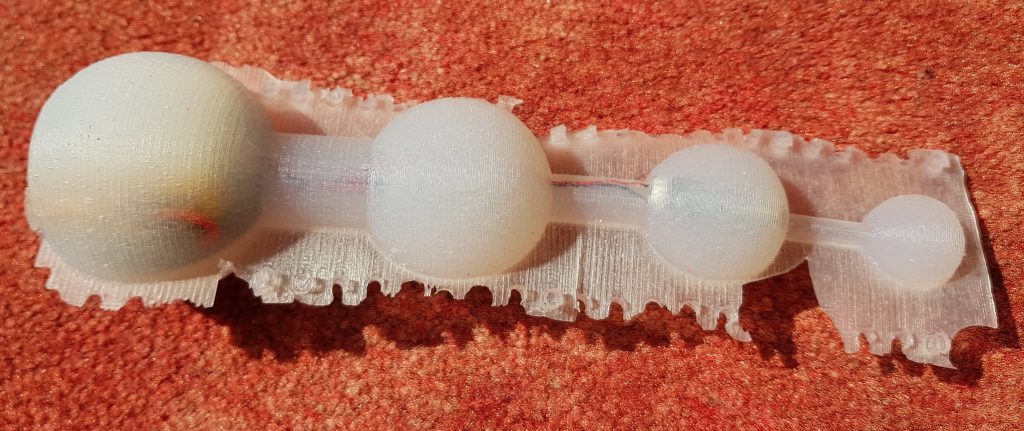
 An alternative to 3d-printed sex toys are silicone toys. For making such a sex toy you need a molding form, where you pour in the silicone. If you use Tinkercad to build the form for the balls motive, you may need more than one hour. If you are not experienced in 3d constrcution it may take days. That’s ok and can be fun as you can realize your fantasies step by step.
An alternative to 3d-printed sex toys are silicone toys. For making such a sex toy you need a molding form, where you pour in the silicone. If you use Tinkercad to build the form for the balls motive, you may need more than one hour. If you are not experienced in 3d constrcution it may take days. That’s ok and can be fun as you can realize your fantasies step by step.
 But if you want to change a detail or want to resize some parts of it, it will take a long time as you have to unbuilt parts of the form, make changes and then reassemble. Sometimes building from scratch is faster.
But if you want to change a detail or want to resize some parts of it, it will take a long time as you have to unbuilt parts of the form, make changes and then reassemble. Sometimes building from scratch is faster.
In the last blog post we have introduced OpenSCAD to construct a sex toy form. Now we want to build a hull for the sex toy for overmolding.
The basic idea is very simple:
- Generate two forms. The smaller one has the size of the sex toy you want to make. The larger one will be the form where you pour in the silicone.
- Than use the OpenSCAD difference command which “subtracts” or cuts out the smaller form from the larger form.
But it is more complicated:
- You have to include a frame otherwise the form would fall over.
- You need two forms (A and b) so you could open the form after molding.
- Both forms must be fastened together when molding. Therefore you need holes for tinkering wire.
 We have created a solution for molding form generation which is as flexible as our OpenSCAD sex toy generator. In addition you can change the thickness of the frame. Therefore you have to change the variable frame_thickness.
We have created a solution for molding form generation which is as flexible as our OpenSCAD sex toy generator. In addition you can change the thickness of the frame. Therefore you have to change the variable frame_thickness.
The SCAD script uses the module base which is already introduced. The generation of the frame is done in the module frame. The frame consists of a base plate and two supporting frames which stabilize the whole form. In addition there are extensions to the frame in the upper part of the form. These extensions will provide holes for fastening both forms.
The module complete_form constructs the form which is tricky. The union command is used to join the complete outer form and the frame. Now we have a filled form and have to remove the inner part. This is done by subtracting another complete form which is a bit smaller than the outer form. This is done with the difference command.
Another module hole provides all holes for the tinkering wire. At last we construct part A and part B of the molding form. Again the difference command is used to cut out one half of the form. This is done by subtracting a cube which is placed in the middle of the complete form. In addition the holes must be subtracted from the complete form.
 You can build in the body interaction vibrator development board to make a vibrating dildo, controlled by motion or by another body interaction vibrator development board. Read more here.
You can build in the body interaction vibrator development board to make a vibrating dildo, controlled by motion or by another body interaction vibrator development board. Read more here.
Try out with the Thingiverse customizer.
Download the zipped SCAD file here: bi1-round12
Or copy and paste the source code to the SCAD software:
// bodyinteraction toy form and mold form generator
// radius of bottom part
r_bottom=25; // [15:5:80]
// height of bottom part
h_bottom=30; // [10:5:80]
// top rounding of bottom part
rounding=10; // [10:5:20]
// radius of ball 1
r_ball1=21; // [15:5:50]
// radius of ball 2
r_ball2=15; // [15:5:50]
//radius of ball 3
r_ball3=11; // [15:5:50]
// radius of connecting cylinders
connector_radius=8; // [10:2:20]
// distance between balls and bottom part
ball_distance=15; // [10:2:40]
// offset (thickness of hull)
o=2;
// thickness of frame
frame_thickness=4;
height=h_bottom+3*ball_distance+r_ball1*2+r_ball2*2+r_ball3*2; echo(height);
// form part A
translate([0,0,height+frame_thickness])rotate([0,180,0])
difference() {
complete_form(r_bottom,h_bottom,rounding,r_ball1,r_ball2,r_ball3,connector_radius,ball_distance,o,frame_thickness,height);
union(){
translate([-r_bottom-o-10,0,-5])
color("red")cube([2*r_bottom+2*o+20,r_bottom+2*o,height+frame_thickness+5]);
holes(height,h_bottom);
}
}
//form part B
translate([90,0,height+frame_thickness])rotate([0,180,0])
difference() {
complete_form(r_bottom,h_bottom,rounding,r_ball1,r_ball2,r_ball3,connector_radius,ball_distance,o,frame_thickness,height);
union(){
translate([-r_bottom-o-10,-r_bottom-o-2-10,-5])
color("red")cube([2*r_bottom+2*o+20,r_bottom+2*o+10,height+frame_thickness+5]);
holes(height,h_bottom);
}
}
module holes (height,h_bottom){
for (i=[h_bottom+30:10:height])
translate([r_bottom-1,5,i])rotate([90,90,0])
color("green")cylinder(h=15,r=1,$fn=20);
for (i=[0:10:h_bottom+20])
translate([r_bottom-3+10,5,i])rotate([90,90,0])
color("blue")cylinder(h=15,r=1,$fn=20);
for (i=[h_bottom+30:10:height])
translate([-r_bottom+1,5,i])rotate([90,90,0])
color("green")cylinder(h=15,r=1,$fn=20);
for (i=[0:10:h_bottom+20])
translate([-r_bottom-6,5,i])rotate([90,90,0])
color("blue")cylinder(h=15,r=1,$fn=20);
}
module complete_form (r_bottom,h_bottom,rounding,r_ball1,r_ball2,r_ball3,connector_radius,ball_distance,o,frame_thickness,height) {
difference() {
union() {
base(r_bottom+o,h_bottom+o,rounding,connector_radius+o,ball_distance-2*o,r_ball1+o,r_ball2+o,r_ball3+o);
//complete frame
frame(2*r_bottom+2*o,o,height,frame_thickness,r_bottom,h_bottom,rounding);
};
base(r_bottom,h_bottom,rounding,connector_radius,ball_distance,r_ball1,r_ball2,r_ball3);
};
}
module frame(width,o,height,frame_thickness,r_bottom,h_bottom,rounding) {
//plate
translate([-width/2,-width/2-2*o,height]) cube(size=[width,width+2*o,frame_thickness]);
//frame1
translate([-width/2,-frame_thickness/2,0]) cube(size=[width,frame_thickness,height]);
//frame 1 extensions
translate([-width/2-010,-frame_thickness/2,-5]) color("blue")cube(size=[12,frame_thickness,60]);
translate([-width/2-10,-frame_thickness/2,55]) color("red")rotate([0,45,0]) cube(size=[12,frame_thickness,20]);
translate([+width/2-2,-frame_thickness/2,-5]) color("green")cube(size=[12,frame_thickness,60]);
translate([+width/2+01,-frame_thickness/2,47]) color("green")rotate([0,-45,0]) cube(size=[12,frame_thickness,20]);
//frame2
translate([-frame_thickness/2,-width/2,0]) cube(size=[frame_thickness,width, ,
height]);
// stabilize bottom with cylinder
color("green")translate([0,0,h_bottom])rotate([00,0,0180])
cylinder(h=r_bottom*2-rounding*.5, r1= r_bottom-rounding, r2=0);
}
module base (r_bottom,height,rounding,connector_radius,ball_distance, c1,c2,c3) {
union () {
// connector
color("white")cylinder(h=height+2*ball_distance+c1*2+c2*2+c3*2,r=connector_radius,$fn=60);
//base
color("DarkSlateBlue") cylinder (h=height-0,r=r_bottom-rounding,$fn=60);
color("MediumSlateBlue")cylinder (h=height-rounding,r=r_bottom,$fn=60);
translate([0,0,height-rounding]) color("SlateBlue") rotate_extrude()
translate([r_bottom-rounding,0,0]) circle(r=rounding,$fn=120);
// circle (ball) 1, 2 and 3
translate([0,0,height+ball_distance+c1]) color("Indigo")sphere(r=c1,center=true,$fn=60);
translate([0,0,height+2*ball_distance+2*c1+c2]) color("Violet")sphere(r=c2,center=true,$fn=60);
translate([0,0,height+3*ball_distance+2*c1+2*c2+c3]) color("Purple")sphere(r=c3,center=true,$fn=60);
}
}
Go to the first part of the SCAD tutorial